Ransomware’s popularity has attracted the attention of cyber criminal gangs; they use these malicious programs in targeted attacks on large organizations in order to steal money. In late 2016, we detected an increase in the number of attacks, the main goal of which was to launch an encryptor on an organization’s network nodes and servers. This is due to the fact that organizing such attacks is simple, while their profitability is high:
- The cost of developing a ransom program is significantly lower compared to other types of malicious software.
- These programs entail a clear monetization model.
- There is a wide range of potential victims.
Today, an attacker (or a group) can easily create their own encryptor without making any special effort. A vivid example is the Mamba encryptor based on DiskCryptor, an open source software. Some cybercriminal groups do not even take the trouble of involving programmers; instead, they use this legal utility “out of the box.”

DiskСryptor utility
The model of attack looks like this:
- Search for an organisation that has an unprotected server with RDP access.
- Guess the password (or buy access on the black market).
- Encrypt a node or server manually.
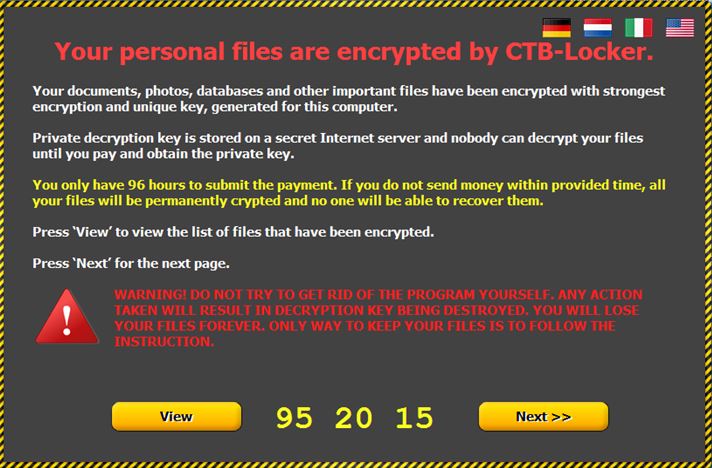
Notification about encrypting the organization’s server
The cost to organize such an attack is minimal, while the profit could reach thousands of dollars. Some partners of well-known encryptors resort to the same scheme. The only difference is the fact that, in order to encrypt the files, they use a version of a ransom program purchased from the group’s developer.
However, true professionals are also active on the playing field. They carefully select targets (major companies with a large number of network nodes), and organize attacks that can last weeks and go through several stages:
- Searching for a victim
- Studying the possibility of penetration
- Penetrating the organization’s network by using exploits for popular software or Trojans on the infected network nodes
- Gaining a foothold on the network and researching its topology
- Acquiring the necessary rights to install the encryptor on all the organization’s nodes/servers
- Installing the encryptor
Read the full story at SecureList.com